- Indications: Joint replacement is typically recommended for individuals who experience severe joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility due to conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or joint injuries.
- Types of Joint Replacement: The most common joint replacement surgeries include knee replacement, hip replacement, and shoulder replacement. Other joints, such as the ankle or elbow, may also be replaced in certain situations.
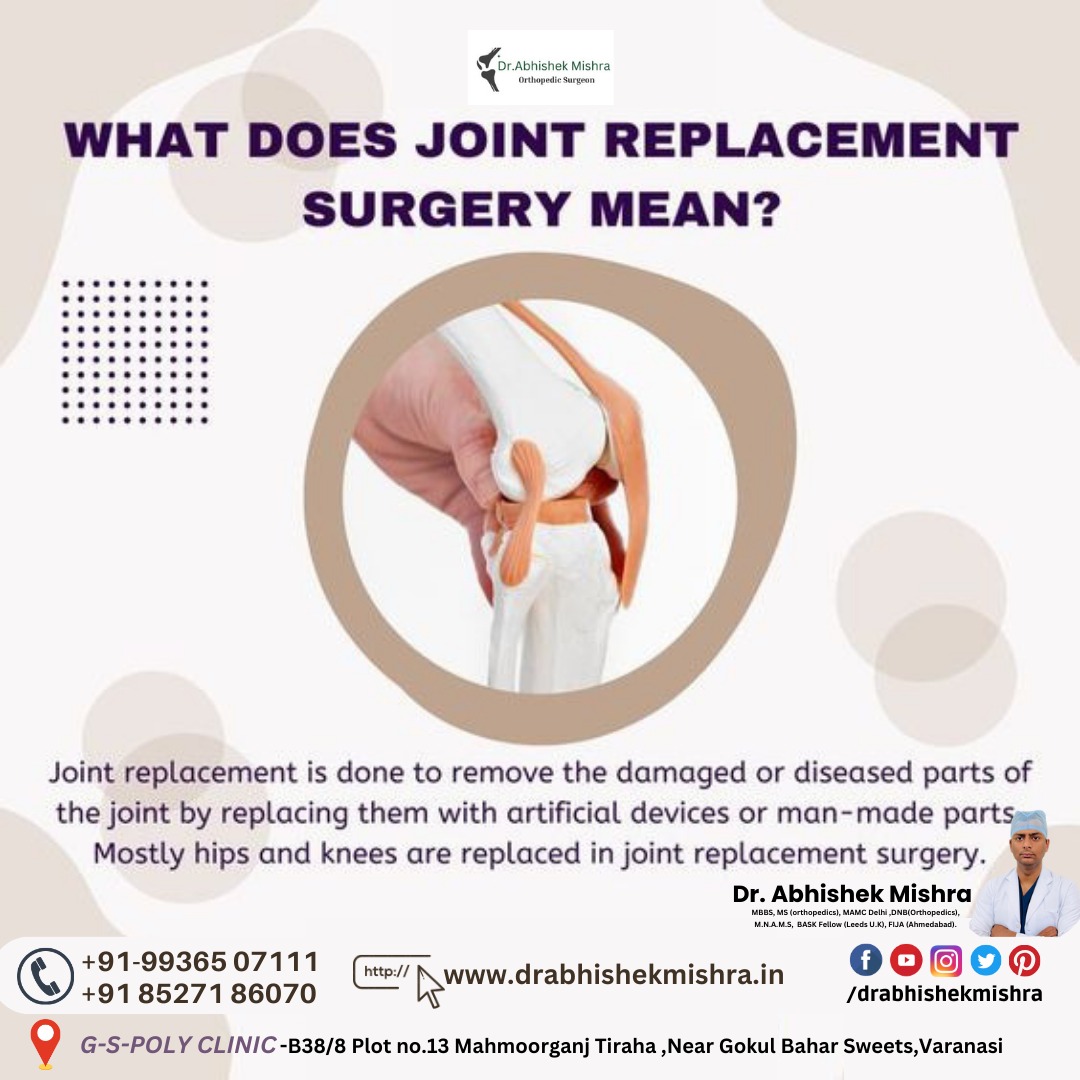
- Procedure: During the surgery, the damaged joint is removed, and the artificial joint is implanted in its place. The goal is to relieve pain, improve joint function, and enhance overall quality of life.
- Materials: The artificial joints are made from materials that are designed to mimic the function of a natural joint. Metal, plastic, and ceramic components are often used, and advancements in materials continue to improve the durability and longevity of joint replacements.
- Recovery: Recovery time varies depending on the type of joint replaced and the individual’s overall health. Physical therapy is usually an essential part of the recovery process to regain strength and range of motion.
- Risks and Complications: Like any surgery, joint replacement carries some risks, including infection, blood clots, and issues related to the artificial joint. However, advancements in surgical techniques and postoperative care have reduced the occurrence of complications.
- Long-Term Outcomes: Many people experience significant improvement in their quality of life after joint replacement surgery. The artificial joints can last for many years, providing relief from pain and restoring function
Categories:
Tags:

No responses yet